Immuno-Diagnostics Antibodies and Antigens for Neurodegenerative Diseases
What are Neurodegenerative Diseases?
Neurodegenerative diseases are defined as diseases described by the progressive dysfunction or death of neurons or nerve cells in the human body. These diseases mainly target the central nervous system meaning the function of the affected body gradually diminishes and reaches a state of severe disability or the patient dies. Some of the familiar brain disorders associated with neurodegenerative diseases are Parkinson's Disease, Alzheimer's Disease and Huntington's Disease [1-3].
The main characteristics of these diseases are:
1. Progressive Deterioration: Symptoms and functions worsen over time.
2. Irreversibility: Currently, most neurodegenerative diseases have no cure, and treatments can only alleviate symptoms and slow disease progression.
3. Multifactorial Etiology: These diseases are influenced by both genetic and environmental as well as lifestyle factors.
Figure 1. Predicting the Unpredictable: The Role of Biomarkers and AI in Early Dementia Detection by Oluwafemidiakhoa / Source: Medium.com
Why is early diagnosis important?
For several reasons, neurodegenerative disease requires early diagnosis and effective treatment.
1. Improving Quality of Life: Early detection and intervention can slow disease progression, alleviate symptoms, and enhance the quality of life for patients.
2. Prolonging Life: Early treatment can extend the life expectancy of patients by delaying the severe outcomes associated with these diseases.
3. Reducing Societal Burden: Early diagnosis and treatment can lower healthcare costs, reduce the economic and psychological burden on patients and their families, and lessen the overall societal impact.
4. Promoting Scientific Research: More cases and data with early diagnosis means more to study disease mechanisms, and hopefully learn how to develop new therapies.
Common Degenerative Diseases
Neurodegenerative diseases are a group of disorders characterized by the gradual degeneration or death of neurons, the fundamental units of the nervous system. These conditions primarily affect the central nervous system, leading to a progressive loss of function, which can ultimately result in severe disability or death. Common neurodegenerative diseases include Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease, and Huntington's disease.
| Biomarker name | Alzheimer's Disease (AD) | Parkinson's Disease (PD) | Huntington's Disease (HD) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phospho-tau181 (p-tau181) | √ | ||
| Phospho-tau217 (p-tau217) | √ | ||
| Phospho-tau231 (p-tau231) | √ | ||
| Phospho-tau212 and 214 (p-tau212 and 214) | √ | ||
| Phospho-tau202 and 205 (p-tau202 and 205) | √ | ||
| Phospho-tau413 (p-tau413) | √ | ||
| Phospho-tau422 (p-tau422) | √ | ||
| Tau proteins (Tau) | √ | √ | |
| Neurofilament light chain (NfL) | √ | √ | √ |
| Glial fibrillary acid protein (GFAP) | √ | √ | |
| Beta-amyloid 42 (Aβ42) | √ | √ | |
| Beta-amyloid 38 (Aβ38) | √ | ||
| Beta-amyloid 40 (Aβ40) | √ | √ | |
| Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1/CCL2) | √ | √ | |
| Neurogranin protein (Neurogranin) | √ | ||
| Neuron-specific enolase (NSE) | √ | ||
| sTREM2 | √ | ||
| Visinin-like protein 1 (VLP-1) | √ | ||
| Chitinase-3-like protein 1 (CHI3L1/YKL-40) | √ | ||
| Alpha-synuclein (α-synuclein) | √ | √ | |
| Apolipoprotein E (APOE4) | √ | ||
| AD-associated neuronal thread protein (AD7c-NTP) | √ | ||
| Human Parkinsonism associated deglycase (PARK7) | √ | √ | |
| Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) | √ | ||
| Interleukin-6 (IL-6) | √ | ||
| Pro-neuropeptide Y | √ | ||
| Heart fatty acid-binding protein (HFABP) | √ |
Technologies and Platforms for Neurodegenerative Diseases Diagnostics
| Technologies and Platforms | Overview | Advantages |
| ELISA (Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay) | It is a commonly used detection technology that determines the presence or absence of specific proteins or other molecules contained in a sample and combines antibodies and an enzyme label. | High sensitivity, strong specificity, simple operation, relatively low cost. |
| Simoa (Single Molecule Array) | Unlike traditional ELISA techniques, this technology can detect very low levels of proteins, nucleic acids and other biomolecules at a sensitivity several orders of magnitudes greater. Through using an array of sealed microwells and fluorescently labeled single molecules, Simoa is able to achieve detection and quantification of individual molecules. This capability is essential for early disease diagnosis, biomarker detection, scientific research[17-19]. | (1) Ultra-high Sensitivity: Simoa can detect biomarkers at extremely low concentrations, even at the single-molecule level, which is several orders of magnitude more sensitive than traditional methods such as ELISA. (2) Early Disease Detection: Due to its high sensitivity, Simoa technology can detect trace biomarkers at very early stages of diseases, facilitating early diagnosis and treatment. (3) Accurate Quantification: Simoa not only detects the presence of biomarkers but also accurately quantifies their concentrations, which is crucial for precise disease monitoring and treatment. (4) Versatility and Flexibility: The application of this technology extends to other biomolecules, such as proteins and nucleic acids, thus it is extremely valuable for a wide range of biomedical research and clinical applications. (5) Reduced Sample Volume: Simoa requires only a very small amount of sample for testing, reducing the need for large sample volumes from patients. (6) High Throughput and Automation: The Simoa platform supports high-throughput sample analysis and can be automated, improving the efficiency and reproducibility of experiments. |
| Multiplex Assays | Simultaneous detection of multiple biomarkers with enhanced detection efficiency and increased data throughput achieved with different fluorescent or chemically labels specifying each biomarker. | High throughput, sample and reagent savings, strong data integration. |
| ECL (Electrochemiluminescence) | A high-sensitivity detection method that combines electrochemical and luminescence technologies to analyze biomarkers and molecular interactions. | Extremely high sensitivity and specificity, low background noise, suitable for detecting low-concentration samples and high-throughput screening. |
| ECLIA (Electrochemiluminescence Immunoassay) | A combined electrochemical-luminescence immunoassay method for biomarker analysis. | Extremely high sensitivity and specificity, suitable for detecting low-concentration samples, low background noise. |
| CLEIA (Chemiluminescent Enzyme Immunoassay) | A chemiluminescence enzyme linked immunoassay (CLIEA) method for detection of biomarkers through a chemical reaction that in a light signal. | High sensitivity, high specificity, rapid detection, suitable for analyzing various sample types. |
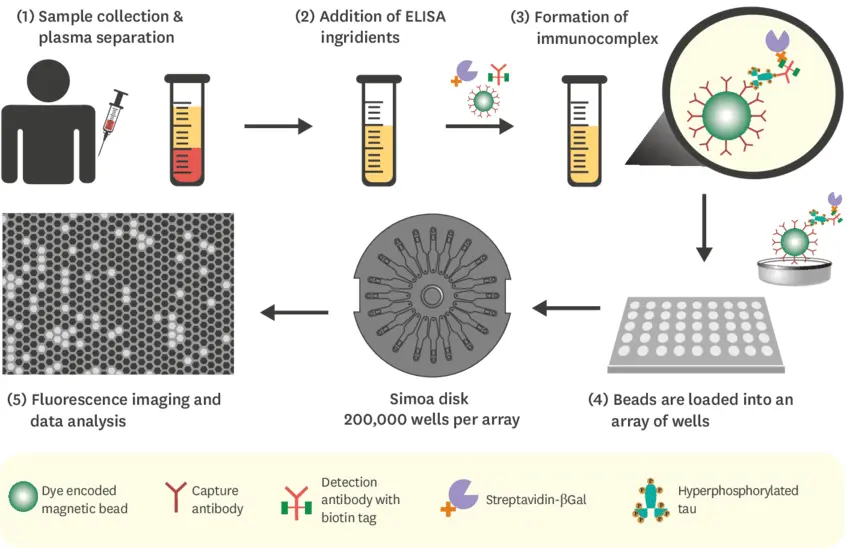
Figure 2. Detecting misfolded proteins in blood through SIMOA technology for the diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease / Source: researchgate.net
GeneMedi's products validation
Click to check the technical information for recommended Antibodies:
Tau Products
Beta-Amyloid
Products
- p-tau181/p-tau217/p-tau231
- Aβ40/Aβ42
Good performance of GeneMedi's p-tau/tau antibodies in ELISA Validation
1. GeneMedi's three phosphorylated tau protein antibodies (p-tau181, p-tau217, and p-tau231) demonstrate outstanding sensitivity and exceptional specificity with their corresponding phosphorylated forms in direct ELISA assays.

GeneMedi's p-tau antibodies and antigens demonstrate excellent binding affinity: GMP-h-p-tau181-Ab01 effectively binds with GMP-h-p-tau181-Ag01, GMP-h-p-tau217-Ab01 binds well with GMP-h-p-tau217-Ag01, and GMP-h-p-tau231-Ab01 shows strong binding with GMP-h-p-tau231-Ag01. These results indicate that GeneMedi's p-tau antibodies and antigens possess outstanding affinity.
Product used as below:
| Cat NO. | Description |
| GMP-h-p-tau181-Ab01 | Anti-Phospho-tau181 (p-tau181) mouse monoclonal antibody (mAb) |
| GMP-h-p-tau181-Ag01 | Phospho-tau181 (p-tau181) antigen (peptide) |
| GMP-h-p-tau217-Ab01 | Anti-Phospho-tau217 (p-tau217) mouse monoclonal antibody (mAb) |
| GMP-h-p-tau217-Ag01 | Phospho-tau217 (p-tau217) antigen (peptide) |
| GMP-h-tau231-Ab01 | Anti-Phospho-tau231 (p-tau231) mouse monoclonal antibody (mAb) |
| GMP-h-p-tau231-Ag01 | Phospho-tau231 (p-tau231) antigen (peptide) |
Fig 1. Validation of GeneMedi's Anti-human p-tau181/p-tau217/p-tau231 antibody in direct ELISA.
A. GeneMedi's GMP-h-p-tau181-Ab01 (Anti-human p-tau181 antibody) is validated to detect the GMP-h-p-tau181-Ag01 (p-tau181 antigen (peptide)) in ELISA, EC50 = 25.26 ng/ml.
B. GeneMedi's GMP-h-p-tau217-Ab01 (Anti-human p-tau217 antibody) is validated to detect the GMP-h-p-tau217-Ag01 (p-tau217 antigen (peptide)) in ELISA, EC50 = 25.85 ng/ml.
C.
GeneMedi's GMP-h-p-tau231-Ab01 (Anti-human p-tau231 antibody) is validated to detect the GMP-h-p-tau231-Ag01 (p-tau231 antigen (peptide)) in ELISA, EC50 = 64.34 ng/ml.
The total tau antibody (GMP-h-TauAb01) does not interact with the p-tau181 (GMP-h-p-tau181-Ag01), p-tau217 (GMP-h-p-tau217-Ag01), and p-tau231 (GMP-h-p-tau231-Ag01) peptide antigen. (Data not shown)
2. In direct ELISA assays, GeneMedi's phosphorylated tau217 antibody demonstrates excellent sensitivity and precision for both full-length and peptide forms of the phosphorylated tau217 antigen. However, its ability to detect other phosphorylated antigens and total tau antigen is limited, indicating its highly specificity.

GeneMedi's GMP-h-p-tau217-Ab01 antibody demonstrates excellent binding ability with the full-length antigen GMP-h-p-tau217-Ag02 as well as the peptide GMP-h-p-tau217-Ag01. However, when interacting with the antigens GMP-h-p-tau181-Ag01, GMP-h-p-tau231-Ag01, and GMP-h-Tau-Ag01, the affinity is relatively weaker, as reflected by significant differences in EC50 values. These results indicate that GeneMedi's p-tau 217 antibody exhibits high affinity and specificity. Product used as below:
| Cat NO. | Description |
| GMP-h-p-tau181-Ag01 | Phospho-tau181(p-tau181) antigen (peptide) |
| GMP-h-p-tau217-Ag01 | Phospho-tau217 (p-tau217) antigen (peptide) |
| GMP-h-p-tau231-Ag01 | Phospho-tau231 (p-tau231) antigen (peptide) |
| GMP-h-p-tau217-Ag02 | Phospho-tau217 (p-tau217) antigen (full length) |
| GMP-h-Tau-Ag01 | Recombinant human MAPT/Tau/MAPTL/MTBT1 Protein |
| GMP-h-p-tau217-Ab01 | Anti-Phospho-tau217 (p-tau217) mouse monoclonal antibody (mAb) |
Fig 2. Direct ELISA Binding Curves of Phosphorylated Tau217 Antibody with Various Antigens.
This graph displays the binding efficiency of the phosphorylated tau217 antibody with five different antigens in an ELISA setup. The x-axis represents the antibody concentration in a logarithmic scale (μg/ml), and the y-axis indicates the corrected absorbance, reflecting the binding efficiency between the antibody and antigens. The data illustrate that GMP-h-p-tau217-Ab01 exhibits high detection efficiency for GMP-h-p-tau217-Ag01 (peptide) with an EC50 of 4.326 ng/ml. For GMP-h-p-tau217-Ag02 (full length), the antibody demonstrates exceptionally high sensitivity, with an EC50 of only 6.943 ng/ml. Additionally, this antibody effectively detects GMP-h-p-tau181-Ag01 (peptide), GMP-h-p-tau231-Ag01 (peptide) and GMP-h-tau-Ag01 (full length) with EC50 values of 27320 ng/ml, 3563 ng/ml and 1843 ng/ml.
3. In sandwich ELISA assays, GeneMedi's p-tau217 antibody and tau antibody pair can detect the full-length phosphorylated 217 protein but are unable to detect phosphorylated 217 peptides or non-phosphorylated proteins.

| Cat NO. | Description |
| GMP-h-p-tau217 A g01 | Phospho-tau217 (p-tau217) antigen (peptide) |
| GMP-h-p-tau217 A g02 | Phospho-tau217 (p-tau217) antigen (full length) |
| GMP-h-p-tau217 Ab01 | Anti-Phospho-tau217 (p-tau217) mouse monoclonal antibody (mAb) |
| GMP-h-p-tau217 Ab02 | Anti-Phospho-tau217 (p-tau217) mouse monoclonal antibody (mAb) |
| GMP-h-tau-A g01 | Recombinant human MAPT/Tau/MA PTL/MTBT1 Protein |
| GMP-h-tauA b01 | A nti-human MAPT/Tau/MA PTL/MTBT1 mouse monoclonal antibody (mAb) |
| GMP-h-tau-A b02 | Anti-human MAPTITau/MA PTL/MTBT1 mouse monoclonal antibody (mAb) |
| GMP-h-tau-A b03 | Anti-human MAPTITau/MA PTL/MTBT1 mouse monoclonal antibody (mAb) |
GMP-h-p-tau217-Ab01 is used as the capture antibody. When GMP-h-Tau-Ab03 is used as the detection antibody, the EC50 for detecting GMP-h-p-tau217-Ag02 is lower than GMP-h-Tau-Ab01, indicating GMP-h-Tau-Ab03 is more suitable as a detection antibody.
However, when detecting phosphorylated 217 peptide GMP-h-p-tau217-Ag01 or non-phosphorylated protein GMP-h-tau-Ag01, the EC50 remains high regardless of whether GMP-h-Tau-Ab03 or GMP-h-Tau-Ab01 is used, suggesting no binding for detecting peptide GMP-h-p-tau217-Ag01 or non-phosphorylated protein GMP-h-tau-Ag01 under these conditions.
Fig3. Sandwich ELISA Analysis of Full-Length Phosphorylated Tau 217 Antigen with Corresponding Phosphorylated Tau 217 Antibody and Total Tau Antibody.
A.This figure illustrates the detection efficacy of two different antibody combinations in Sandwich ELISA experiments targeting the GMP-h-p-tau217-Ag02 antigen (full length). The x-axis represents the antigen concentration displayed on a logarithmic scale (μg/ml), while the y-axis shows the corrected absorbance. The results indicate that the combination of GMP-h-p-tau217-Ab01 as the coating antibody and GMP-h-Tau-Ab01 as the detection antibody yields an EC50 of 76.55 ng/ml. Conversely, using GMP-h-p-tau217-Ab01 as the coating antibody and GMP-h-Tau-Ab03 as the detection antibody results in an EC50 of 39.02 ng/ml, demonstrating higher detection sensitivity at lower concentrations.
B.This figure demonstrates the detection results of two different detection antibodies (GMP-h-tau-Ab01 and GMP-h-tau-Ab03) against the GMP-h-tau-Ag01 antigen (full length) in an ELISA assay, using GMP-h-p-tau217-Ab01 as the coating antibody. The x-axis represents antigen concentration, displayed on a logarithmic scale (μg/ml); the y-axis shows corrected absorbance. The results reveal that when using GMP-h-tau-Ab03 as the detection antibody, the EC50 value reaches 20030 ng/ml, indicating a lower sensitivity to the antigen; whereas, when using GMP-h-tau-Ab01 as the detection antibody, the EC50 value soars to 4352000 ng/ml, demonstrating poor efficacy in detecting the antigen.
C. This figure illustrates the detection performance of four different antibody combinations in an ELISA assay targeting the GMP-h-p-tau217-Ag01 antigen (peptide). The x-axis represents antigen concentration, displayed on a logarithmic scale (μg/ml), while the y-axis shows the corrected absorbance. The curves in the figure show that all antibody combinations maintain relatively consistent absorbance changes across a range of low to high concentrations, indicating these results also reveal that the sensitivity of these four antibody combinations in detecting the GMP-h-p-tau217-Ag01 (peptide) antigen is relatively low.
4. GeneMedi's Tau Protein antibodies exhibit remarkable sensitivity and exceptional specificity when tested with GeneMedi’s recombinant human Tau Protein in direct ELISA assays.
Fig4. Validation of GeneMedi's Anti-human Tau antibody.
GeneMedi's GMP-h-Tau-Ab01/03/05/06/07/08/09/10/11/12 (Anti-human Tau antibody) is validated to detect the GMP-h-Tau-Ag01 (Recombinant human Tau Protein) in ELISA.

5. In sandwich ELISA assays, GeneMedi's p-tau217/tau antibody pairs can detect the full-length phosphorylated 217 protein but are unable to detect the non-phosphorylated full-length Tau protein
Fig5. Sandwich ELISA Analysis of Full-Length Phosphorylated Tau 217 Antigen with Corresponding Phosphorylated Tau 217 Antibody and Total Tau Antibody.
These figures illustrate the detection efficacy of different antibody combinations in Sandwich ELISA experiments targeting the GMP-h-p-tau217-Ag02 antigen (full length). The results show that when using GMP-h-Tau-Ab01 (A), GMP-h-Tau-Ab03 (B), GMP-h-Tau-Ab05 (C), and GMP-h-Tau-Ab06 (D), GMP-h-Tau-Ab07 (E), GMP-h-Tau-Ab08 (F), GMP-h-Tau-Ab09 (G), GMP-h-Tau-Ab10 (H), GMP-h-Tau-Ab11 (I) and GMP-h-Tau-Ab12 (J) respectively as the detection antibodies, and GMP-h-p-tau217-Ab01/03/05/06 as the coating antibody in each case. As a negative control, when the same antibody pairs target the GMP-h-Tau-Ag01 antigen (full length), the resulting EC50 is NA, which demonstrates their high specificity and sensitivity.
The table shows the EC50 values of different antibody combinations in sandwich ELISA experiments targeting the GMP-h-p-tau217-Ag02 antigen (full-length), as shown in A–J. GMP-h-p-Tau217-Ab06 shows the best EC50 in almost all antibody pairs.

6. Validation of High-Specificity p-Tau217/181/231 and Tau Antibody Pairs
The ELISA validation data demonstrates the exceptional specificity of p-Tau217/181/231 and tau antibody pairs: p-Tau217/Tau pair exclusively recognizes p-Tau217 full-length antigen (Figure A); p-Tau181/Tau pair shows selective binding to p-Tau181 full-length antigen (Figure B); p-Tau231/Tau pair specifically detects p-Tau231 full-length antigen (Figure C). The complete absence of cross-reactivity with non-target phospho-Tau isoforms confirms the superior specificity of these antibody pairs, making them ideal for precise Alzheimer's disease biomarker detection.
Fig6. High specificity and reliability of p-Tau217/181/231 and tau antibody pairs In ELISA.
A. p-Tau217/ tau antibody pair binds specifically to p-Tau217 full-length antigen.
B. p-Tau181/ tau antibody pair binds specifically to p-Tau181 full-length antigen.
C. p-Tau231/ tau antibody pair binds specifically to p-Tau231 full-length antigen.

7. High specificity and reliability of pTau217/181/231 Phosphorylated full-length protein
GeneMedi is proud to offer pTau217/181/231 phosphorylated full-length protein. As shown in Figures A, B, and C: p-Tau217 full-length antigen specifically binds to p-Tau217 antibodies (Figure A); p-Tau181 full-length antigen specifically binds to p-Tau181 antibodies (Figure B); p-Tau231 full-length antigen specifically binds to p-Tau231 antibodies (Figure C). These results demonstrate that pTau217/181/231 phosphorylated full-length antigens are phosphorylated at their respective sites, with minimal phosphorylation at other sites, ensuring high specificity and reliability for research and diagnostic applications.
Fig7. High specificity and reliability of p-Tau217/181/231 Phosphorylated Full-Length Antigens In ELISA.
A. p-Tau217 full-length antigen binds specifically to p-Tau217 antibodies.
B. p-Tau181 full-length antigen binds specifically to p-Tau181 antibodies.
C. p-Tau231 full-length antigen binds specifically to p-Tau231 antibodies.

Good performance of GeneMedi's Aβ40/Aβ42 antibodies in ELISA and CLIA Validation
The high-performance Aβ40 and Aβ42 antibody raw materials developed by GeneMedi have the advantages of good specificity and high sensitivity, and are the preferred raw materials for the development of in vitro diagnostics reagents for Alzheimer's disease.
In direct ELISA analysis, GMP-h-Aβ40-Ab01 and GMP-h-Aβ42-Ab01 can Recognizes Aβ40 or Aβ42 with high specificity. GMP-h-Aβ42-Ab02 has cross-reactivity with both Aβ40 and Aβ42.
In CLIA verification, the antibody pair (Capture: GMP-h-Aβ40-Ab01 , Detect: GMP-h-Aβ42-Ab02 ) can detect the GMP-h-Aβ40-Ag01, and the antibody pair (Capture: GMP-h-Aβ42-Ab02 , Detect: GMP-h-Aβ42-Ab01 ) can detect the GMP-h-Aβ42-Ag01. Beta-amyloid(1-42) antibodies (GMP-h-Aβ42-Ab02 and GMP-h-Aβ42-Ab01) established a standard curve, and the detection range of Aβ42 was 100-1700 pg/mL.
Figure 1: Good performance of GeneMedi's Aβ40/Aβ42 antibodies in ELISA and CLIA Validation
A. GMP-h-Aβ40-Ab01 and GMP-h-Aβ42-Ab02 can bind GMP-h-Aβ40-Ag01, while GMP-h-Aβ42-Ab01 can not bind the Aβ40 antigen in direct ELISA.
B. GMP-h-Aβ42-Ab01 and GMP-h-Aβ42-Ab02 can bind GMP-h-Aβ42-Ag01, while GMP-h-Aβ40-Ab01 can not bind the Aβ42 antigen in direct ELISA.
C. CLIA verification data of the antibody pair (Capture: GMP-h-Aβ40-Ab01 , Detect: GMP-h-Aβ42-Ab02 ) to detect the GMP-h-Aβ40-Ag01.
D. CLIA verification data of the antibody pair (Capture: GMP-h-Aβ42-Ab02 , Detect: GMP-h-Aβ42-Ab01 ) to detect the GMP-h-Aβ42-Ag01.

Reference
- [1] Dugger BN, Dickson DW. Pathology of Neurodegenerative Diseases. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2017 Jul 5;9(7):a028035.
- [2] Temple S. Advancing cell therapy for neurodegenerative diseases. Cell Stem Cell. 2023 May 4;30(5):512-529. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2023.03.017. Epub 2023 Apr 20.
- [3] Agnello L, Ciaccio M. Neurodegenerative Diseases: From Molecular Basis to Therapy. Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 25;23(21):12854.
- [4] Maccioni, Ricardo B., Juan P. Muñoz and et al. "The molecular bases of Alzheimer's disease and other neurodegenerative disorders." Archives of medical research 32.5 (2001): 367-381.
- [5] Monzio Compagnoni, Giacomo, et al. "The role of mitochondria in neurodegenerative diseases: the lesson from Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease." Molecular neurobiology 57 (2020): 2959-2980.
- [6] Khan, Asmat Ullah, et al. "Awareness and current knowledge of Parkinson's disease: a neurodegenerative disorder." International Journal of Neuroscience 129.1 (2019): 55-93.
- [7] Ramesh, Sairam, and Arosh S. Perera Molligoda Arachchige. "Depletion of dopamine in Parkinson's disease and relevant therapeutic options: A review of the literature." AIMS neuroscience 10.3 (2023): 200.
- [8] Kaye, Julia, Terry Reisine, and Steve Finkbeiner. "Huntington's disease mouse models: Unraveling the pathology caused by CAG repeat expansion." Faculty reviews 10 (2021).
- [9] Bano, D., et al. "Neurodegenerative processes in Huntington's disease." Cell death & disease 2.11 (2011): e228-e228.
- [10] Palmqvist S, Janelidze S, Quiroz YT. Discriminative Accuracy of Plasma Phospho-tau217 for Alzheimer Disease vs Other Neurodegenerative Disorders. JAMA. 2020 Aug 25;324(8):772-781.
- [11] Thijssen EH, La Joie R, Wolf A. Advancing Research and Treatment for Frontotemporal Lobar Degeneration (ARTFL) investigators. Diagnostic value of plasma phosphorylated tau181 in Alzheimer's disease and frontotemporal lobar degeneration. Nat Med. 2020 Mar;26(3):387-397.
- [12] Baiardi S, Quadalti C, Mammana A. Diagnostic value of plasma p-tau181, NfL, and GFAP in a clinical setting cohort of prevalent neurodegenerative dementias.
- [13] Mielke MM, Dage JL, Frank RD. Performance of plasma phosphorylated tau 181 and 217 in the community. Nat Med. 2022 Jul;28(7):1398-1405.
- [14] Gonzalez MC, Ashton NJ, Gomes BF, et al. Association of Plasma p-tau181 and p-tau231 Concentrations With Cognitive Decline in Patients With Probable Dementia With Lewy Bodies. JAMA Neurol. 2022;79(1):32–37.
- [15] NfL blood test may detect neurodegeneration in youngsters.
- [16] Mayer CA, Brunkhorst R, Niessner M and et al. Blood levels of glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) in patients with neurological diseases. PLoS One. 2013 Apr 23;8(4):e62101.
- [17] Wu, Connie, Adam M. Maley, and David R. Walt. "Single-molecule measurements in microwells for clinical applications." Critical Reviews in Clinical Laboratory Sciences 57.4 (2020): 270-290.
- [18] Rivnak, Andrew J., et al. "A fully-automated, six-plex single molecule immunoassay for measuring cytokines in blood." Journal of immunological methods 424 (2015): 20-27.
- [19] Wu, Connie, Padric M. Garden, and David R. Walt. "Ultrasensitive detection of attomolar protein concentrations by dropcast single molecule assays." Journal of the American Chemical Society 142.28 (2020): 12314-12323.






 Full List Download
Full List Download 


 Facebook
Facebook LinkedIn
LinkedIn Twitter
Twitter
